When your body activates your immune system, it sends out inflammatory cells. Chronic, low-level inflammation might be the SILENT culprit behind your aging process. There is growing evidence that there’s a correlation between chronic systemic inflammation and chronic disease, such as:
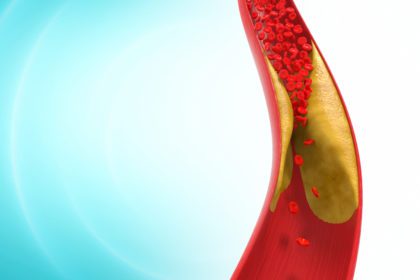
- Coronary atherosclerosis (plaque buildup)
- Stroke
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Macular degeneration (a common form of age-related blindness)
- Asthma
- Dementia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Some cancers
- Depression
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation
Chronic, low-level inflammation is quite different from acute inflammation, the body’s healthy response to injury and infection. When you get a bug bite or sprained ankle and the area becomes swollen, warm, painful, and red, your body is trying to defend itself by sending immune cells and key nutrients to the area. Your inflammatory cells are attacking bacteria or healing damaged tissue. This is an acute inflammatory response.
The Silent Killer
If your body sends out inflammatory cells when you’re not sick, injured, or there’s no outside danger, you may have chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is imperceptible and dangerous and a symptom of many chronic diseases, like arthritis and Alzheimer’s disease. It can damage body systems silently for weeks, months, and even a lifetime depending on the chronic disease. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory cells and substances attack joint tissues leading to an inflammation that comes and goes. This can then cause pain and severe damage to joints.
Chronic inflammation is long term — it lasts for months to years.
How Inflammation Predicts Cardiac Risk
Studies have shown a correlation between heart disease and elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a protein in your blood that signals inflammation. According to the Cleveland Clinic, measuring CRP is at least as predictive as cholesterol in assessing cardiac risk. Following an anti-inflammatory diet consists of a high fiber intake which has been shown to lower CRP levels.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods

Researchers have identified certain foods that can cause as well as combat inflammation. Many of the anti-inflammatory foods are found in the so-called Mediterranean diet (including these top five heart-healthy) that focus on fresh, whole, unprocessed foods.