Lifestyle Diseases are Linked to Severe Coronavirus Infection
In Louisiana, 41% of deaths from COVID-19 had diabetes.
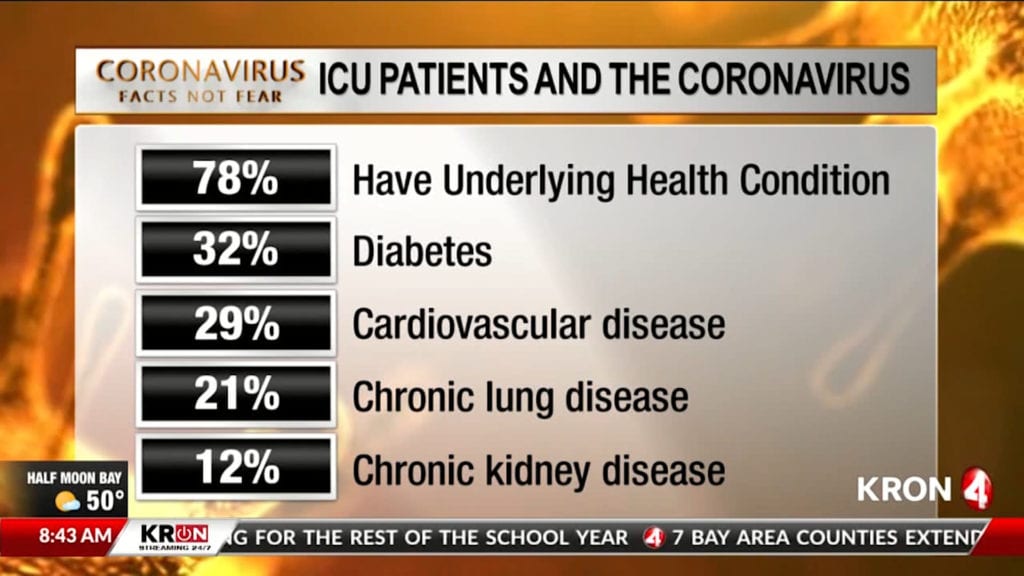
According to CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report March 31, 78% of ICU patients with COVID-19 have at least one underlying health condition:
- 32% – Have diabetes
- 29% – Have heart disease
- 21% – Have chronic lung disease
- 12% – Have chronic kidney disease
- 9% – Have a weakened immune system (immunocompromised)
A Healthy Gut Promotes a Healthy Immune System
80% of your immune system is in the gut. Keeping it healthy is a proactive way to fight off infections faster and better.
Many inflammatory diseases are lifestyle diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, chronic lung disease). A lifestyle disease is a medical condition or disorder that’s associated with the way in which a person lives. Inflammatory diseases are linked to a “malfunctioning gut” (too many of the bad bacteria).
Specific Nutrients that Contribute to Immune Function
- Antioxidant vitamins (vitamins A, B6, folate, B12, C, D, E)
- Trace elements (selenium, copper, iron, zinc).
According to a study published in the Frontiers in Physiology, adults ages 65 to 79 showed small increases in T cells (white blood cells that fight disease) when they followed a Mediterranean-type of diet and took 400 IU of vitamin D for one year.
There is evidence that various micronutrient deficiencies, e.g., deficiencies of zinc, selenium, iron, copper, folic acid, and vitamins A, B6, C, and E — alter immune responses in animals. The human response has not yet been assessed.
Foods that Feed the Gut
Certain foods build up good bacteria in your gut, which in turn, support a healthy gut and immune system.
These foods include: probiotics, prebiotics, and polyphenols. At the same time these types of foods are effective at preventing and managing cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and chronic inflammation.
1. Probiotics (foods with live bacterial cultures) — Probiotics are good bacteria in food. They can help your gut bacteria stay in “equilibrium” and may help strengthen the immune system and improve gut health (ease irritable bowel syndrome).
- Yogurt (with live and active cultures), kefir
- Fermented plant foods, i.e., kimchi, kombucha, raw (not pasteurized) sauerkraut, miso, tempeh
2. Prebiotics (whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes) — Prebiotics boost the growth of good bacteria. Think FIBER! Foods most beneficial to the gut microbiome* are those that contain dietary fibers (a large class of non-digestible carbohydrates).
*Microbiome is where all the bacteria (both good and bad) in your digestive tract live. The large intestine is one “large bacterial ecosystem” that protects, strengthens, and nourishes you.
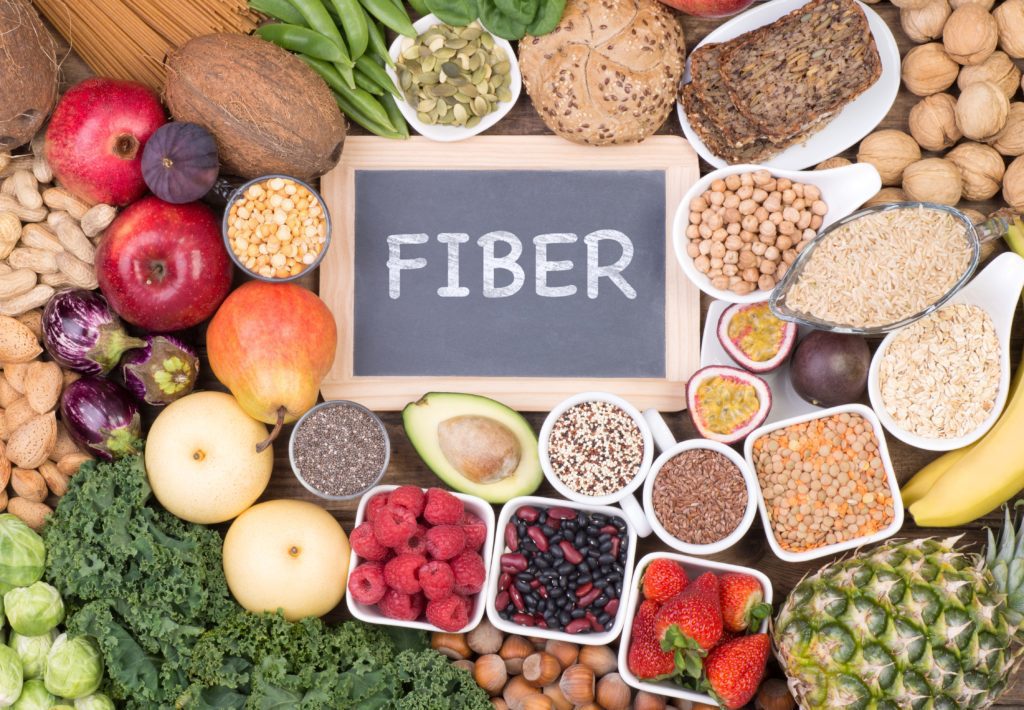

Examples of prebiotics:
- Whole grains
- Bananas, onions, garlic, leeks
- Asparagus, artichokes, soybeans (tofu, edamame)
3. Polyphenols — Beneficial compounds in many plant foods which are also packed with antioxidants, such as:
- Fruits
- Vegetables (particularly cauliflower)
- Herbs, spices (turmeric)
- Tea, wine
- Dark chocolate (70% cacao or higher)

![]() Karen’s Fit Tip: Each one of us can play a significant role in flattening the coronavirus curve by not only observing the things the CDC has recommended, but by taking care of ourselves in terms of nutrition, exercise, sleep and stress management —- all these things play a part in our fight against this virus.
Karen’s Fit Tip: Each one of us can play a significant role in flattening the coronavirus curve by not only observing the things the CDC has recommended, but by taking care of ourselves in terms of nutrition, exercise, sleep and stress management —- all these things play a part in our fight against this virus.